Registration form for a free trial class
• Teacher will find a perfect path for your child
• You can explore our platform
• Your child will love our fun interactive lessons
• You can explore our platform
• Your child will love our fun interactive lessons
Golden Friday: Learn more - pay less!
Golden Friday - ITGenio’s autumn Black Friday event
Join now and get up to 2 months of free learning with your subscription plan.
Choose 6 or 12 months - the longer you study, the bigger your bonus.
Join now and get up to 2 months of free learning with your subscription plan.
Choose 6 or 12 months - the longer you study, the bigger your bonus.
Subscription = continuous learning with fixed lessons per month and up to 44%
savings compared to standard packages.
Submit your request → our manager will help you activate your bonus.
savings compared to standard packages.
Submit your request → our manager will help you activate your bonus.
Reasons to study Python

Python has a big future in AI programming, machine learning, data analysis and game development. Many popular services such as Instagram, Netflix, Google, etc. use it and need a lot of Python developers.
In-Demand Programming Language

Your child spends a lot of time online? Make this hobby useful! By learning Python, your child will learn how to create their own games, solve logic problems and gain a much better understanding how the computer works.
Useful Hobby

Python at ITGENIO is a sure and easy step on programming journey. Our tutors make sure your child will be able to develop critical thinking skills, boost creativity, improve knowledge in related areas such as math.
Good Place to Start
Python course is perfect for children that:



Want to try their first text-based programming language
Consider taking an Python course at a university
Want to develop analytical and logical thinking and participate in coding competitions
A student at the end of the Python course:

Understands programming fundamentals: libraries, architecture, algorithms
Develops problem-solving skills
Practices breaking down problems into smaller, manageable parts
Has practical experience with Python language and modules




01. Block Python
Python course modules
4 modules for kids of different age and coding background. A student can take between one and four modules depending on their skills.

Recommended for children switching from Scratch or Minecraft to Python. Designed to prepare students for complex text-based Python programming. Suits 9+ year-olds without knowledge of the programming basics.
This module is suitable for children who have completed Scratch course and are ready to code. To sign up for this module children must be able to read well, understand theoretical materials and think logically. The course is aimed at children of 10 years old and older. Kids under the age of 13 must take a test before signing up for the course.

PyGame is an additional course to Python programming. It includes improving object-oriented programming skills, as well as FPS, rendering and other skills that are used in game-making process. It is suitable for children from 10 years old.

For this module the student should have a good knowledge of Python, preferably should have already completed at least one of our Python courses. Flask is a framework for Python that helps with the creation of full-fledged websites. It suits 12-year-olds and older kids.



Python course curriculum
Elementary
10-20 lessons
Basic
20-30 lessons
Advanced
30-40 lessons




Data input and output and mathematics

Basic development environment for Python, creating, running and saving programs. Variable. Integer and string. Print and input functions. Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division. Integer division. Division without remainder. Remainder of division, rounding.
Importing modules. Math, random, turtle modules
Built-in ready-made modules, advanced math, random numbers, and drawing algorithms. Ways to import modules. Using out-of-the-box functions from modules.
Conditions
Boolean data type. Comparison operators. Construct if-elif-else. Logical operators. The student will learn how to make simple, nested, and complex conditional constructions.
While loop
The while loop. An infinite loop. Break and continue loop control operators. The student will learn how to use loop control operators and variable-counters, and make a loop with a condition inside.
Strings
Actions with strings, indexes, and slices. Finding, counting, and replacing characters. Letters, managing letter cases and numbers in strings.
For loop

The student will learn how to run through words and sentences and generate numeric ranges.
Lists
The student will learn what lists are, how to find the maximum and minimum values in a list of items, and how to sort lists according to various criteria.
Additional modules
Working with text files on your computer, features of working with date and time, third-party modules. The open function. The pickle module. The datetime and time module. Terminal and installation of custom modules via the pip package manager. The pillow module.
Functions
The student will learn how to create functions, use arguments and parameters, and how to return a result from a function.
Designing a graphical user interface using the tkinter library
Label, Button, Frame, LabelFrame, Entry, Listbox, Toplevel, Scale widgets. Widget configuration. Basics of interface design, window creation, ready-made widgets (button, input field and other elements), connection of widgets with program functionality.
Dictionaries
The student will learn how to create empty dictionaries, dictionaries with "key-value" pairs, get values by key, add a new pair to an existing dictionary, modify values, delete the last pair, delete pairs by their keys, clear the dictionary completely, and go through the keys and values.
Designing a graphical user interface using the tkinter library

Delayed function triggering, lambda expressions, exception handling and the interactive messagebox sub-module. Exception handling: try, except, finally. Messagebox. The bind, forget and destroy methods. The pyinstaller module.
Sets
The student will learn how to create a set, how to convert other data types into a set, how to find out if sets are equal, what are the properties of sets, how to find out if a set belongs to a set and the power of a set.
Designing a graphical user interface using the tkinter library
Creating a canvas and drawing geometric shapes. Changing and removing objects, calling functions, creating labels. Handling intersections and undoing delayed triggering. Drawing lines and changing coordinates with coords. The study of the tkinter module will continue with the creation of a new widget — Canvas that allows one to draw shapes and handle their intersections.
Designing a graphical user interface using the tkinter library
The module will explore the concept of "modularity", which allows you to create one large project from several smaller modules. Radiobutton, Checkbutton and Spinbox widgets.
Two-Dimensional Arrays
The student will study two-dimensional arrays, find ways to apply matrices, and solve a number of problems with them.
Object-oriented programming
The student will use the example of game classes (Warrior, Mage, etc.) to understand what classes are, why to use them and what benefits they provide.
Additional modules
Additional sections are given depending on the student’s preferences. The requests library and BeautifulSoup4. Web parsing basics. Telebot or discord library. Creating a bot for Telegram or Discord and running the bot on Heroku. The basics of Git. Versions, creating a repository on Github, commands init, add, commit, remote, push and others.
Meet ITgenio tutors — Python experts that are passionate about children and their subject
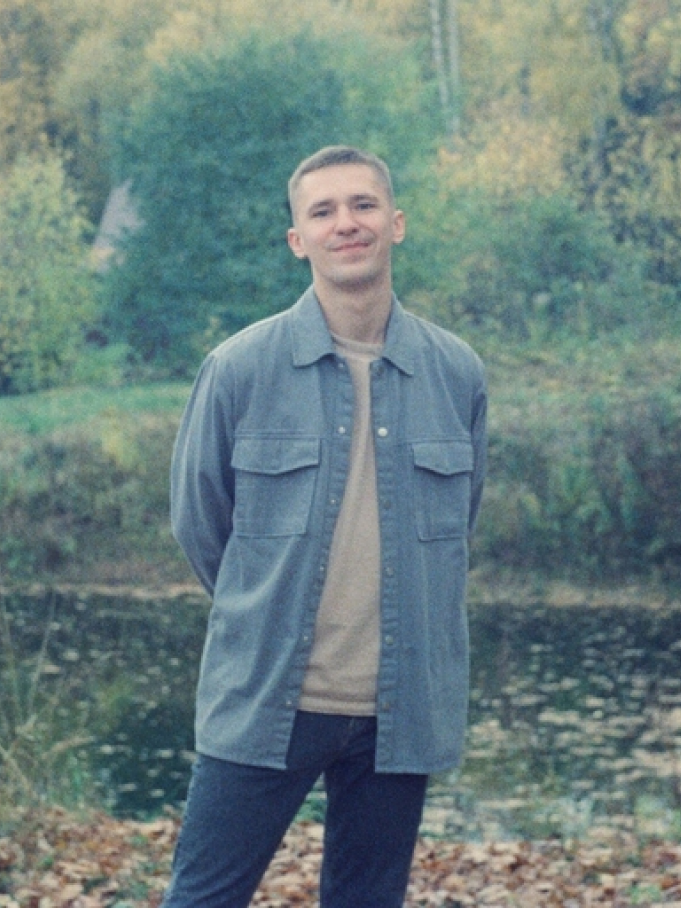





Yury Herasimovich
About Python course
About our tutors
Top tutor
Our students are trained by experienced tutors and active professionals in IT technologies, machine learning, neural networks, analytics, and mathematics. Our tutors also prepare the students for programming competitions and olympiads.








Only one out of every fifty candidates becomes a tutor at ItGenio
The tutor will become not only a mentor but also a friend to your child
Interesting facts about the course:
Python is among the top 5 programming languages. The largest global companies use Python, including Google, IBM, Yahoo, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, Mozilla, Dropbox, Pinterest, YouTube, and many others.
Python is among the top 5 programming languages. The largest global companies use Python, including Google, IBM, Yahoo, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, Mozilla, Dropbox, Pinterest, YouTube, and many others.


Education: BS in Electrical Engineering (electric drives & robotics)
Interesting facts about the course:
Python is among the top 5 programming languages. The largest global companies use Python, including Google, IBM, Yahoo, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, Mozilla, Dropbox, Pinterest, YouTube, and many others.
Python is among the top 5 programming languages. The largest global companies use Python, including Google, IBM, Yahoo, Netflix, Spotify, Amazon, Mozilla, Dropbox, Pinterest, YouTube, and many others.
Choose a larger package, pay less per class
Change between subjects without any fees
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
$20,90/lesson
$334.4 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
$18,90/lesson
$604.8 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
$16,90/lesson
$1081.6 total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
$14,90/lesson
$1907.2 total cost
-39%
-31%
-23%
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
$18,5/lesson
$296.00 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
$16,9/lesson
$540.80 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
$14,9/lesson

$953.60 total cost
Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
$13,5/lesson
$1728 total cost
-39%
-23%
-31%
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
$16,50/lesson
$264,00 USD total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
$14,90/lesson
$476,80 USD total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
$13,50/lesson

$864,00 USD total cost
Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
$11,90/lesson
$1523,20 USD total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
$13,9/lesson
$222.40 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
$12,9/lesson
$412.80 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
$11,5/lesson

$736.00 total cost
Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
$10,5/lesson
$1344.00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
$12,90/lesson
$206,40 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
$11,90/lesson
$380,80 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
$10,50/lesson

$672,00 total cost
Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
$9,50/lesson
$1216,00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
€15,90/lesson
€254.40 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
€14,50/lesson
€464.00 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
€12,90/lesson
€825.60 total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
€11,90/lesson
€1523.20 total cost
-40%
-24%
-33%
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
€14,50/lesson
€232,00 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
€12,90/lesson
€412,80 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
€11,50/lesson
€736,00 total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
€10,50/lesson
€1344,00 total cost
-40%
-24%
-33%
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
£14,97/lesson
£239.47 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
£13,67/lesson
£437.51 total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
£12,05/lesson
£771.47 total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
£10,92/lesson
£1397.96 total cost
-39%
-23%
-30%
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
1050 RUB/lesson
16800.00 RUB total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
950 RUB/lesson
30400.00 RUB total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
890 RUB/lesson
56960.00 RUB total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
850 RUB/lesson
108800.00 RUB total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
16 lessons
32,5 BYN/lesson
520.00 BYN total cost
Master a course or start a second one
32 lessons
28,5 BYN/lesson
912.00 BYN total cost
Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
64 lessons
25,9 BYN/lesson
1657.60 BYN total cost

Use a strong portfolio and skillset to prepare for paid projects
128 lessons
23,5 BYN/lesson
3008.00 BYN total cost
We suggest having basic PC user skills for joining group lessons

Groups have max. 6 students, the tutor works with each student

Prices for 1-hour lessons are shown, 2-hour lessons also available

Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
$38,50/lesson
$552.00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
$34,90/lesson
$1008.00 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
$31,50/lesson
$1760.00 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
$27,50/lesson
$3187.20 total cost
-39%
-23%
-31%
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
$34,50/lesson
$552.00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
$31,50/lesson
$1008.00 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
$27,50/lesson
$1760 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
$24,90/lesson
$3187.20 total cost
-39%
-23%
-31%
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
$30,50/lesson
$488,00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
$27,50/lesson
$880,00 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
$24,90/lesson
$1593,60 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
$21,90/lesson
$2803,20 total cost
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
$25,90/lesson
$414.40 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
$23,90/lesson
$764.80 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
$21,50/lesson
$1376.00 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
$19,50/lesson
$2496.00 total cost
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
$23,90/lesson
$382,40 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
$21,90/lesson
$700,80 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
$19,50/lesson
$1248,00 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
$17,50/lesson
$2240,00 total cost
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
€29,50/lesson
€472.00 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
€26,90/lesson
€860.80 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
€23,90/lesson
€1529.60 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
€21,90/lesson
€2803.20 total cost
-40%
-24%
-33%
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
€26,90/lesson
€430,40 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
€23,90/lesson
€764,80 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
€21,50/lesson
€1376,00 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
€19,50/lesson
€2496,00 total cost
-40%
-24%
-33%
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
£27,91/lesson
£446.57 total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
£25,48/lesson
£815.48 total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
£22,25/lesson
£1423.85 total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
£20,14/lesson
£2578.46 total cost
-39%
-23%
-30%
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
1950 RUB/lesson
31200 RUB total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
1750 RUB/lesson
56000 RUB total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
1650 RUB/lesson
105600 RUB total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
1590 RUB/lesson
203520 RUB total cost
Practice the basics and deal with course selection
16 lessons
59,9 BYN/lesson
958.40 BYN total cost
Gain solid knowledge and publish a project
32 lessons
52,90 BYN/lesson
1692.80 BYN total cost
Master a course or start a second one
64 lessons
47,90 BYN/lesson
3065.60 BYN total cost

Explore multiple subjects and build a strong portfolio
128 lessons
43,50 BYN/lesson
5568.00 BYN total cost
Suitable for beginners as well

Your child will get all the attention and detailed feedback by the tutor

Private lessons last 1 hour

By submitting this form you agree with the privacy policy and accept the public offer agreement
Sign up for a free first Python class
230,000+ lessons per year
Discover other ITGENIO CODING courses
A high salary and more career opportunities in the future

Development of logical thinking

Learning an in-demand profession

Scratch Junior
Introduce your child to coding in a fun and engaging way
Computer literacy
Build a foundation of essential digital skills in a nurturing environment
5+
7+
Minecraft
Developing imagination and problem-solving skills in virtual worlds
9+
Python FAQ
Answers to the most popular questions
Depending on the level of initial experience, children either start from gradually learning the most basic elements of programming, getting an understanding of data structures, how the data input and output function, what variables and loops are, or enhance their level and grow their skills by designing a graphical user interface, studying two-dimensional arrays and other functionality that Python has to offer.
But regardless of whether the child is new to programming or it’s not his first steps, the learning process is based on a holistic approach, facilitating progression from simple to more complex ideas, includes interactive examples and exercises to help kids learn, and the ongoing support of teachers, who are careful to ensure that all material is thoroughly understood.
But regardless of whether the child is new to programming or it’s not his first steps, the learning process is based on a holistic approach, facilitating progression from simple to more complex ideas, includes interactive examples and exercises to help kids learn, and the ongoing support of teachers, who are careful to ensure that all material is thoroughly understood.
How do Python programming courses for kids work?
Q:
A:
It depends on the individual's interest, however, it's recommended that students are at least 10 years old.
What age is appropriate for starting to study the Python language?
Q:
A:
Here are a few popular books that are designed to teach kids how to code in Python:
It's important to note that some books may be more suitable for certain age groups or skill levels, so it's a good idea to check the level of difficulty or ask our teachers before purchasing any book.
- "Python for Kids: A Playful Introduction to Programming" by Jason R. Briggs.
- "Hello World!: Computer Programming for Kids and Other Beginners" by Warren Sande and Carter Sande.
- "Python for Everybody: Exploring Data in Python 3" by Dr. Charles Severance.
- "Coding Games in Python" by Al Sweigart.
It's important to note that some books may be more suitable for certain age groups or skill levels, so it's a good idea to check the level of difficulty or ask our teachers before purchasing any book.
Which Python books are the right choice for kids?
Q:
A:
Operating System: Windows 8/8.1/10 x64, Mac OS 10.12 or later;
• Installed browser Google Chrome;
• RAM: 4 GB (recommended 8 GB);
• Processor 2-core with a clock frequency of 2.2 GHz (preferably 4-core if possible);
• Hard disk space: at least 4-6 GB of free hard disk space;
• Screen resolution: preferably 1280x800 pixels;
• Microphone or headset;
• Speakers;
• Internet connection from 1 Mbps.
• Installed browser Google Chrome;
• RAM: 4 GB (recommended 8 GB);
• Processor 2-core with a clock frequency of 2.2 GHz (preferably 4-core if possible);
• Hard disk space: at least 4-6 GB of free hard disk space;
• Screen resolution: preferably 1280x800 pixels;
• Microphone or headset;
• Speakers;
• Internet connection from 1 Mbps.
What are the system requirements?
Q:
A:
- Python is the foundation for popular games and is the preferred language around the world for developing captivating AI and Machine Learning apps. Besides, it’s easy and straightforward syntax is perfect to be a gentle introduction to programming for children.
- After completing the online Python course for kids students are able to try themselves in IT-related jobs like web developing. Children develop independent projects and strengthen their Python knowledge.
- By studying coding children improve analytical thinking, logic and creativity, and develop independent decision-making. Besides, all our online Python classes for kids are designed with the child's psychology in mind and fuel childrens motivation, as well as encourage them to persist.
- Python is in the top-5 most popular programming languages today. It is used by such companies as Google and Instagram. Learning this language gives your kid an opportunity to develop websites, games, applications and system tools.
What are the benefits of studying Python?
Q:
A:






